Verifying someone’s identity used to mean checking a password, an ID card, or a phone number. But as digital interactions grow and risks increase, these old methods don’t always hold up. That’s where biometric verification comes in.
It’s not just about unlocking phones anymore as businesses are now using biometrics like facial recognition, fingerprints, and voice patterns to make sure users are exactly who they claim to be. It’s faster, more secure, and harder to fake.
In this blog, we’ll explore what biometric verification actually means, the different types, how it’s being used across industries, and why it’s quickly becoming a must-have for modern businesses.
What is Biometric Verification?
Biometric verification is the process of confirming a person’s identity using their unique biological traits. Unlike passwords or PINs, which can be guessed or stolen, biometric data is much harder to replicate. It relies on characteristics that are unique to each individual, like your fingerprint, face, voice, or even the way you walk.
What makes it so powerful is that it eliminates the need for users to remember anything or carry physical documents. This not only improves security but also creates a smoother user experience, especially during onboarding, logins, and access control.
Whether you’re running a financial platform, managing employee access, or operating a high-risk online service, biometric verification offers a reliable as well as scalable way to verify users with speed and confidence.

How Does Biometric Verification Work?
At its core, biometric verification involves capturing a biometric sample (like a fingerprint or facial scan), converting it into a digital template, and then comparing it to a stored template in a database. If there is a match, the user is authenticated.
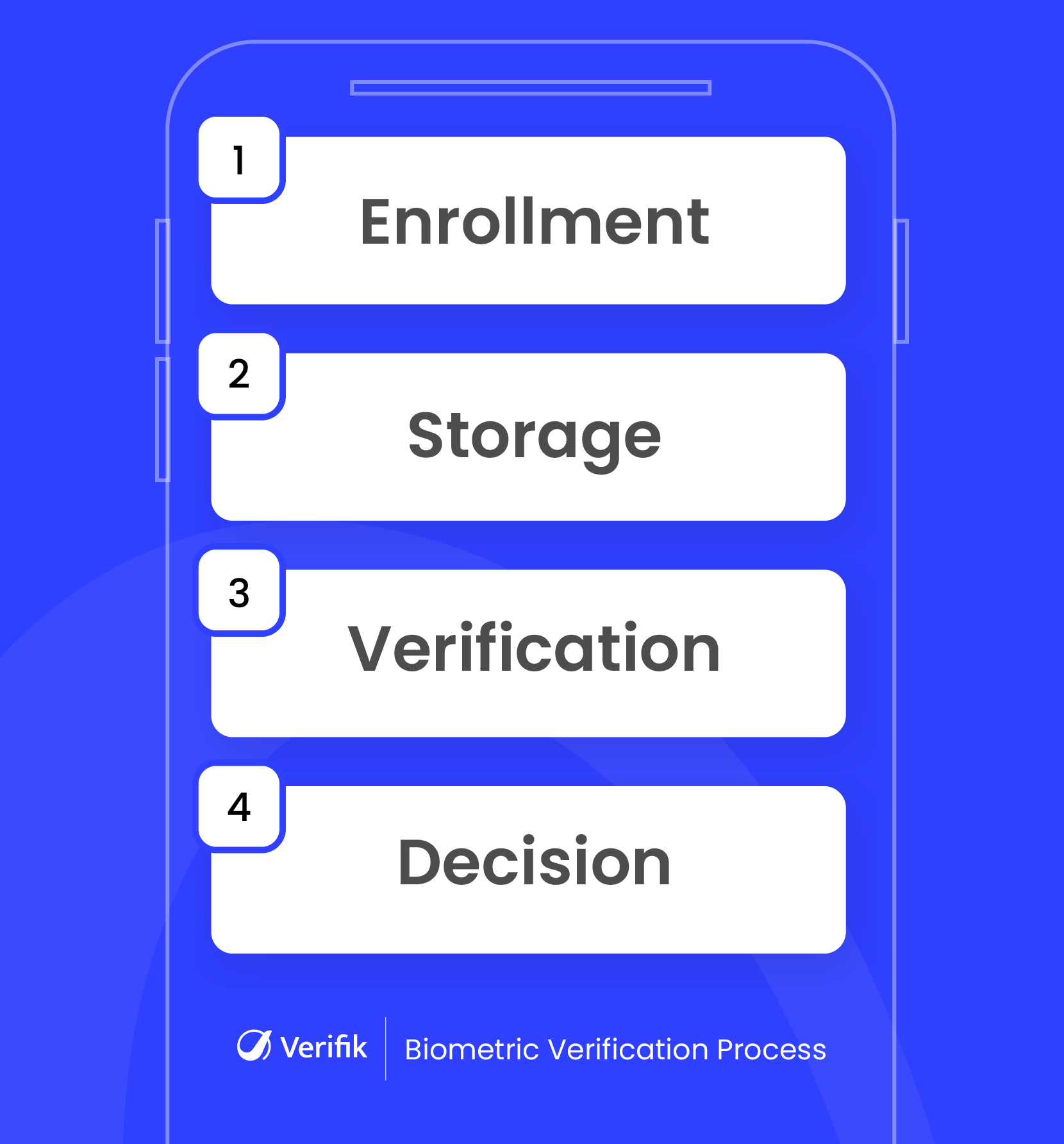
The process usually follows these steps:
- Enrollment: The user’s biometric data is captured and securely stored as a template.
- Storage: This template is stored in a secure database or encrypted locally on a device.
- Verification: When access is requested, the system captures a new biometric sample and compares it to the stored template.
- Decision: If the samples match within a threshold, access is granted; if not, access is denied.
To learn in detail about the process of implementing biometric verification in your business, check out our blog: How to Implement Biometric Verification in Your Business.
Types of Biometric Verification
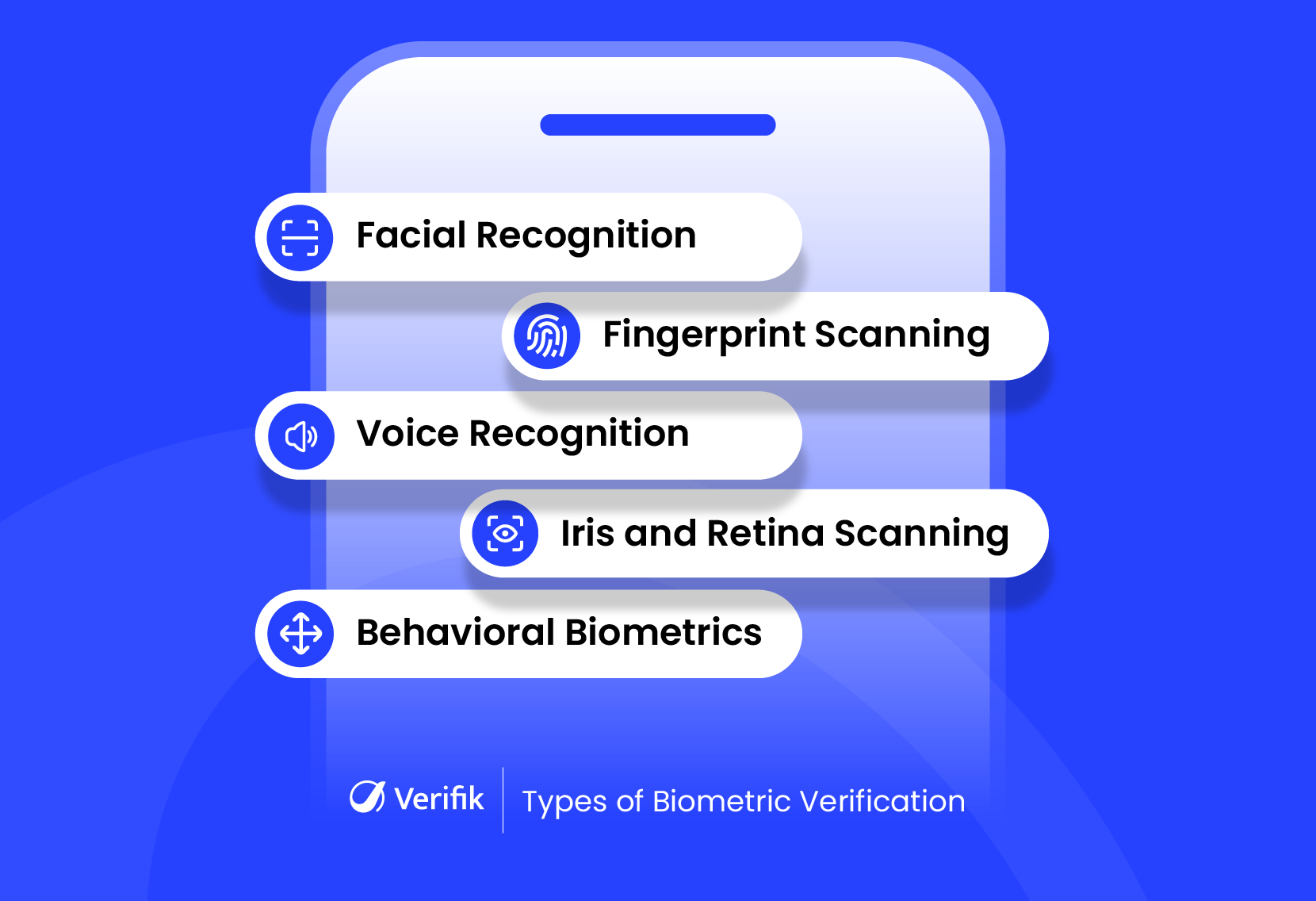
Biometric verification isn’t limited to one method. Depending on the use case and level of security needed, businesses can choose from a variety of biometric modalities. Here are the most common ones:
1. Facial Recognition
One of the most widely used methods today, facial recognition analyzes the geometry of a person’s face, like the distance between the eyes, shape of the jawline, and contour of the nose. It allows for fast, contactless identity verification and is widely used in remote onboarding and access control scenarios.
Modern identity verification solutions have enhanced facial recognition with features like liveness detection, which ensures the presence of a real user and prevents spoofing through images or video.
Some of the most innovative advancements in this space is ZK Face Proof, the world’s first and only technology that combines facial recognition with zero-knowledge proofs. Since there is no storage of raw facial biometrics, it prevents cyber attacks and data theft while enabling instant, hassle-free access.
2. Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint verification has long been a go-to method in both consumer devices and enterprise systems. It’s accurate and easy to use, though it requires physical contact, which might not be ideal for all environments.
Fingerprint recognition captures the unique ridge patterns on a person’s finger. It’s widely used in access systems and mobile devices due to its speed and affordability.
However, its reliance on physical contact and susceptibility to wear-and-tear or spoofing makes it less suitable for contactless or high-security environments.
3. Voice Recognition
This method analyzes the tone, pitch, and rhythm of a user’s voice to create a unique vocal profile. It’s especially useful in call centers, voice assistants, and other voice-driven platforms, providing a convenient and hands-free way to verify identity.
Voice recognition adds an extra layer of security during phone-based interactions and can be combined with other biometric factors for multi-factor authentication. However, background noise and voice changes due to illness can sometimes affect accuracy.
4. Iris and Retina Scanning
These methods scan the intricate patterns in the eye’s iris or the retina at the back of the eye, which are unique to each individual and extremely difficult to replicate. Commonly used in government, defense, and high-security facilities, these technologies offer very high accuracy and reliability.
However, they require specialized, often expensive hardware, which limits their accessibility for everyday use. Additionally, the scanning process can be intrusive or slower compared to other biometric methods, sometimes causing discomfort or inconvenience for users.
5. Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics focus on how users interact with their devices, such as typing patterns, mouse movements, or even walking style. This approach offers continuous, real-time verification by monitoring behavior throughout a session, making it highly effective for detecting fraud and preventing unauthorized access.
Because it works silently in the background, it strengthens security without interrupting users, making it an increasingly popular choice for seamless and reliable identity verification. However, it may require some time to accurately learn a user’s behavior, which can affect initial accuracy.
For a deeper look into how biometric verification is used in the business world, read our blog: Top 10 Biometric Verification Use Cases in Businesses.
Use Cases of Biometric Verification in Business
Biometric verification is transforming the way businesses secure their operations and interact with customers. From enhancing security to improving user experience, these technologies offer a wide range of practical applications across industries.
1. Access Control: Physical and Digital Security
Biometric systems like fingerprint and facial recognition are widely used to regulate access to physical locations such as offices and data centers. These methods offer a more secure alternative to traditional keys or passcodes, as biometric traits are unique and difficult to replicate.
Additionally, biometric verification is increasingly used to secure digital access by ensuring that only authorized users can enter sensitive systems, applications, and networks. Contactless biometric options also enhance hygiene and convenience, which is increasingly important in modern work environments.
2. Digital Onboarding and Customer Authentication
With remote services becoming the norm, biometric verification plays a crucial role in enabling seamless and secure digital onboarding for customers.
Facial recognition technology can quickly verify a person’s identity using just a smartphone camera, thus eliminating the need for physical documents or in-person visits. This accelerates account opening or service activation in industries like banking, insurance, and telecommunications.
Furthermore, privacy-focused advancements ensure that sensitive biometric data is protected, which helps in building customer trust.
3. Fraud Prevention and Transaction Security
Financial institutions and online retailers increasingly rely on biometric verification to protect accounts and transactions.
Facial recognition, especially when combined with privacy-first technologies that avoid centralized storage of raw biometric data, helps accurately confirm user identity while safeguarding personal information. These systems can quickly detect and flag suspicious activity during authentication to prevent fraud before it happens.
This approach not only reduces financial losses but also helps organizations meet strict regulatory compliance standards.
4. Workforce Management and Attendance Tracking
Biometric solutions are widely used for tracking employee attendance and managing work hours more accurately than manual logs or badge swipes.
Fingerprint or facial recognition clocks ensure that attendance data is reliable and tamper-proof, reducing “buddy punching” where one employee clocks in for another. These systems streamline payroll processing, simplify compliance with labor laws, and provide managers with better insights into workforce productivity.
5. Improved User Experience
Biometric verification improves user experience by enabling fast and effortless authentication. Touchless options like facial recognition or behavioral biometrics remove the need to remember passwords or carry physical tokens, thereby reducing user frustration.
For employees, this means smoother access to devices, applications, or premises. For customers, it means quicker service and fewer barriers during login or payment processes. The result is a more efficient, secure, and user-friendly environment that benefits everyone involved.

Benefits of Biometric Verification for Businesses
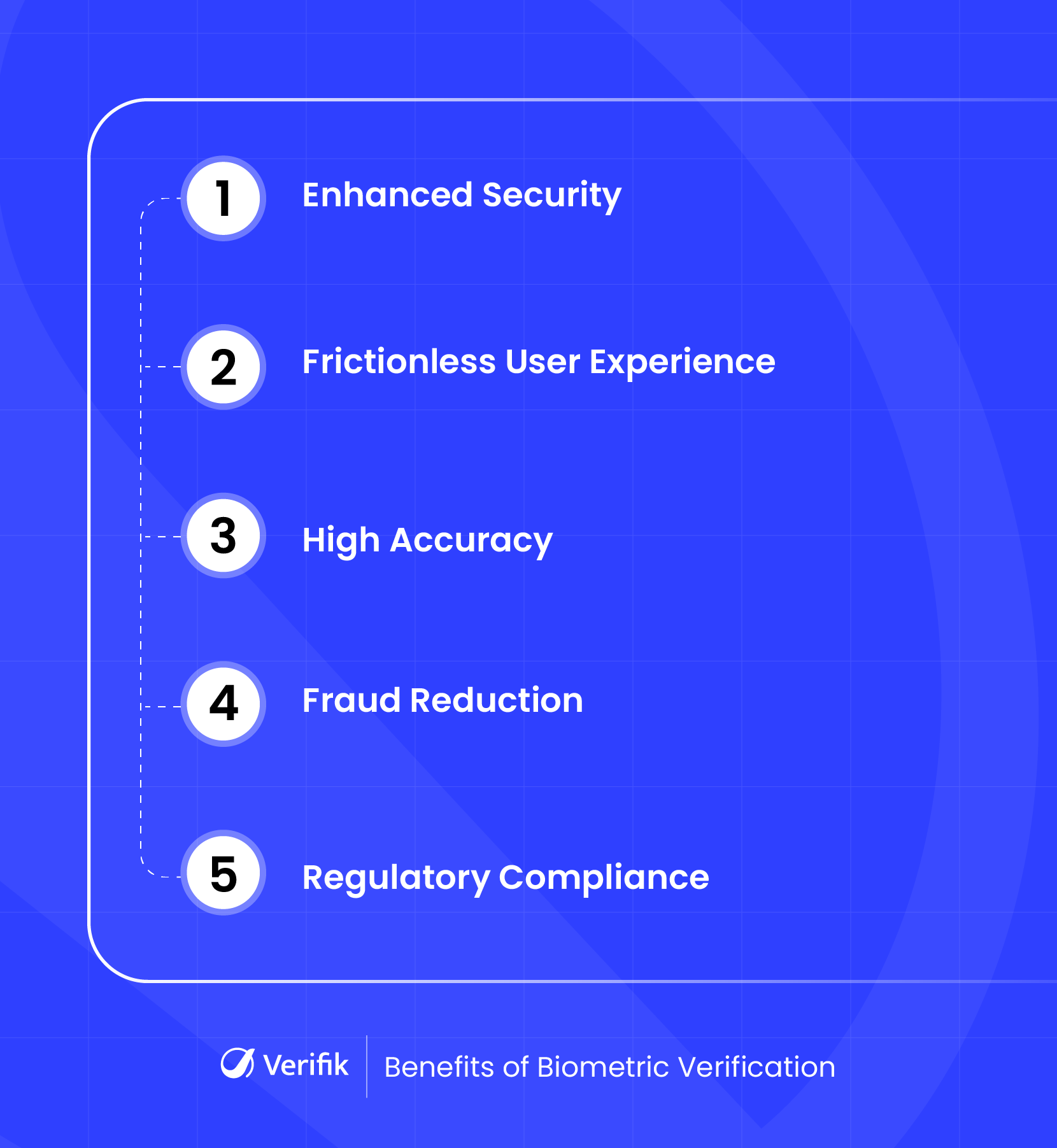
Biometric verification brings together security, speed, and accuracy to help businesses verify users more confidently while reducing fraud and friction. Here are some of the most valuable benefits it offers:
1. Enhanced Security
One of the strongest advantages of biometric verification is the level of security it offers. Unlike passwords or PINs, which can be guessed, shared, or stolen, biometric data is unique to each individual. A fingerprint, face, or voice pattern can’t be replicated easily, making it much harder for bad actors to impersonate users.
For businesses, it means having full visibility and control over who is accessing their platforms, hence significantly reducing the risk of identity fraud, unauthorized logins, and data breaches.
2. Frictionless User Experience
Today’s users expect fast, simple, and secure interactions. Biometric verification makes that possible. Whether it’s logging in with a face scan or verifying identity with a fingerprint, the process takes just seconds and requires little effort from the user. There’s no need to remember passwords, scan QR codes, or wait for OTPs.
For businesses, this translates into higher user satisfaction, smoother onboarding, and fewer drop-offs during sign-up or authentication processes.
3. High Accuracy
When implemented correctly, especially when paired with AI or machine learning, biometric verification systems deliver exceptional accuracy. Modern solutions can distinguish between subtle biometric patterns and even predict user age with surprising precision.
This helps businesses confidently verify users, reduce errors in the onboarding process, and ensure that the right people are gaining access to their platforms.
4. Fraud Reduction
Biometric systems are designed not just to verify, but to protect. Technologies like liveness detection help confirm that a real person, not a photo, video, or deepfake, is present during verification. This layer of defense is crucial in today’s threat landscape, where synthetic identities and AI-generated media are increasingly being used for fraud.
Businesses using biometric verification with built-in anti-spoofing tools can detect these attempts early and block them before damage is done.
5. Regulatory Compliance
From GDPR and KYC to COPPA and AML directives, regulatory pressure on identity verification has increased globally. Biometric verification helps businesses meet these standards by offering strong proof of identity and supporting secure data handling.
Many modern biometric systems also provide audit trails and encrypted data storage, making it easier to comply with regional and industry-specific requirements. For regulated industries like fintech, gaming, or healthcare, this isn’t just a benefit, it’s often a necessity.
Challenges to Consider in Biometric Verification
While biometric verification offers powerful benefits, businesses should be aware of a few key challenges to ensure successful implementation.
-
Privacy Concerns
One of the most common concerns around biometrics is data privacy. Unlike passwords, biometric traits are deeply personal and cannot be changed if compromised. This makes users understandably cautious.
To address this, forward-thinking companies are turning to ZK Face Proof, the most advanced form of Zero Knowledge Proof technology. It verifies users through a simple facial scan without storing any biometric or sensitive information to ensure complete privacy and compliance by design.
-
False Negatives and Positives
Biometric systems, while highly accurate, aren’t immune to occasional errors. A false negative may deny access to a legitimate user, while a false positive may incorrectly approve someone who shouldn’t get through. These edge cases can disrupt user experience and damage trust.
That’s why systems must be trained on diverse data sets and continuously fine-tuned to handle various real-world scenarios, such as aging faces, lighting conditions, or temporary changes in appearance.
-
Device Variability
Another challenge lies in the diversity of devices consumers use. A biometric system that works flawlessly on a high-end smartphone might struggle on older models or laptops with low-quality cameras.
To deliver a consistent experience, businesses must ensure their biometric solutions are device-agnostic; optimized to work across a wide range of hardware, operating systems, and camera types. This ensures accessibility for all users, regardless of the tech in their hands.
Final Words
Biometric verification has quickly moved from a futuristic concept to a practical necessity for modern businesses. Whether it’s securing user accounts, streamlining onboarding, or preventing fraud, biometrics offer a smarter, faster, and more reliable way to verify identity. The key is to choose the right biometric identity verification solution that fits your security needs without compromising user convenience.
Secure Your Business with Verifik’s Biometric Verification
Ready to take your identity verification to the next level? Verifik offers cutting-edge biometric solutions designed specifically for businesses like yours. Our exclusive ZK Face Proof technology ensures maximum security without compromising user privacy. From real-time facial recognition and document validation to passwordless logins, Verifik has solutions that make identity verification seamless and fraud-resistant.
Get in touch today for a free demo and discover how Verifik can protect your platform, reduce fraud, and help you build trust with your customers.