We unlock our phones with a glance or a tap. We pass through airport gates without handing over a passport. Biometric verification technology is quietly reshaping how we prove who we are, and two methods are leading the way: facial recognition and fingerprint identification.
Both are fast and secure, but they serve different needs. The real question is which one fits better for your specific use case, whether it’s for access control, identity verification, or onboarding.
In this blog, we’ll break down how each technology works, compare them side by side, and help you figure out which one is the right fit for your businesses. Let’s get into it!
What Is Fingerprint Identification?
Fingerprint identification is one of the most established forms of biometric verification. It works by capturing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on a person’s fingertip and comparing those features against stored records to confirm identity.
For businesses, it’s a proven method used in everything from employee time tracking to securing access to sensitive systems and physical spaces. It’s valued for its speed, accuracy, and relatively low cost of deployment.
How It Works:
-
Image Capturing
A fingerprint sensor or scanner collects a detailed image of the fingertip’s surface. These can be optical, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors depending on the use case.
-
Data Mapping
The system analyzes the image to identify unique data points, such as ridge endings, bifurcations, and patterns. These minutiae points are then converted into a digital template.
-
Matching & Verification
The extracted template is compared against a database of enrolled fingerprints. If the match score meets a set threshold, identity is confirmed.
Common Business Use Cases:
-
Workforce Management
Used in attendance systems to prevent time fraud and eliminate buddy punching.
-
Access Control
Grants secure entry into office buildings, data centers, and restricted work areas.
-
Device and App Security
Embedded in laptops, smartphones, and POS terminals to authorize transactions and protect user accounts.
-
Banking and Government Services
Used to verify citizens during KYC checks, social service distribution, and ATM withdrawals in various countries.
Advantages for Businesses:
-
Fast and Accurate
Matches are typically completed in milliseconds, making it ideal for high-frequency verification.
-
Cost-Effective at Scale
Hardware costs are relatively low, and the systems are easy to integrate into existing workflows.
-
Familiar to End Users
Many people already use it on personal devices, so adoption is frictionless.
Limitations to Consider:
-
Requires Physical Contact
Direct contact with the scanner raises hygiene concerns and increases maintenance needs in high-touch environments.
-
Environmental Sensitivity
Dust, grease, moisture, or damaged fingerprints (common in manual labor sectors) can affect scan quality and lead to false rejections.
-
Not Ideal for High-Volume Entry Points
Fingerprint systems can slow down entry when large groups need to authenticate at the same time.
What is Facial Recognition?
Facial recognition is an advanced biometric technology that identifies or verifies a person by analyzing the unique geometry of their face. It maps specific facial features, such as the distance between the eyes, nose shape, cheekbone contours, and jawline, to create a digital facial signature that can be compared with stored templates.
For businesses, facial recognition technology offers a touchless, user-friendly, and fast method of authentication, ideal for both physical and digital access.The demand for facial recognition is only accelerating. By 2025, the facial recognition market size is expected to reach $5.73 billion, and by 2031, it’s projected to more than double. That’s because businesses want authentication that works instantly, scales easily, and doesn’t get in the user’s way.

How It Works:
-
Image Capturing
A camera captures a real-time image or video of a person’s face.
-
Face Detection
The facial recognition software’s AI algorithm identifies and isolates the face from the background and other objects.
-
Data Mapping
The system then measures and digitizes key facial landmarks, such as the eye distance, cheekbone structure, and nose position, to create a unique biometric template.
-
Matching & Verification
That template is compared against existing templates in the system’s database to confirm or deny identity.
Common Business Use Cases:
-
Touchless Office Entry
Speed up entry and exit in corporate offices, co-working spaces, and high-security zones without requiring physical contact or ID cards.
-
Digital Customer Verification
Quickly and securely onboard users or authorize high-risk actions in banking, fintech, telecom, and insurance applications.
-
Airport ID Checks
Replace manual document checks with real-time face scans for faster and more secure identity verification at gates and borders.
-
Event Access Management
Verify attendees instantly and manage large crowds more efficiently with face-based check-in at conferences, concerts, and expos.
Advantages for Businesses:
-
Touchless Office Entry
Speed up entry and exit in corporate offices, co-working spaces, and high-security zones without requiring physical contact or access cards.
-
Digital Customer Verification
Quickly and securely onboard users or authorize high-risk actions in banking, fintech, telecom, and insurance applications.
-
Frictionless and Fast
Identity checks happen quickly and smoothly, so operations keep running without interruptions and customers experience less wait time.
-
Highly Scalable
Whether your business serves hundreds or millions of users, facial recognition scales effortlessly to handle identity checks in real time without impacting performance.
Limitations to Consider:
-
Sensitive to Environmental Factors
Verification accuracy may decline in poor lighting or when users wear masks, hats, or heavy makeup.
-
Data Privacy Concerns
Businesses must manage facial data responsibly to comply with privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, or LGPD.
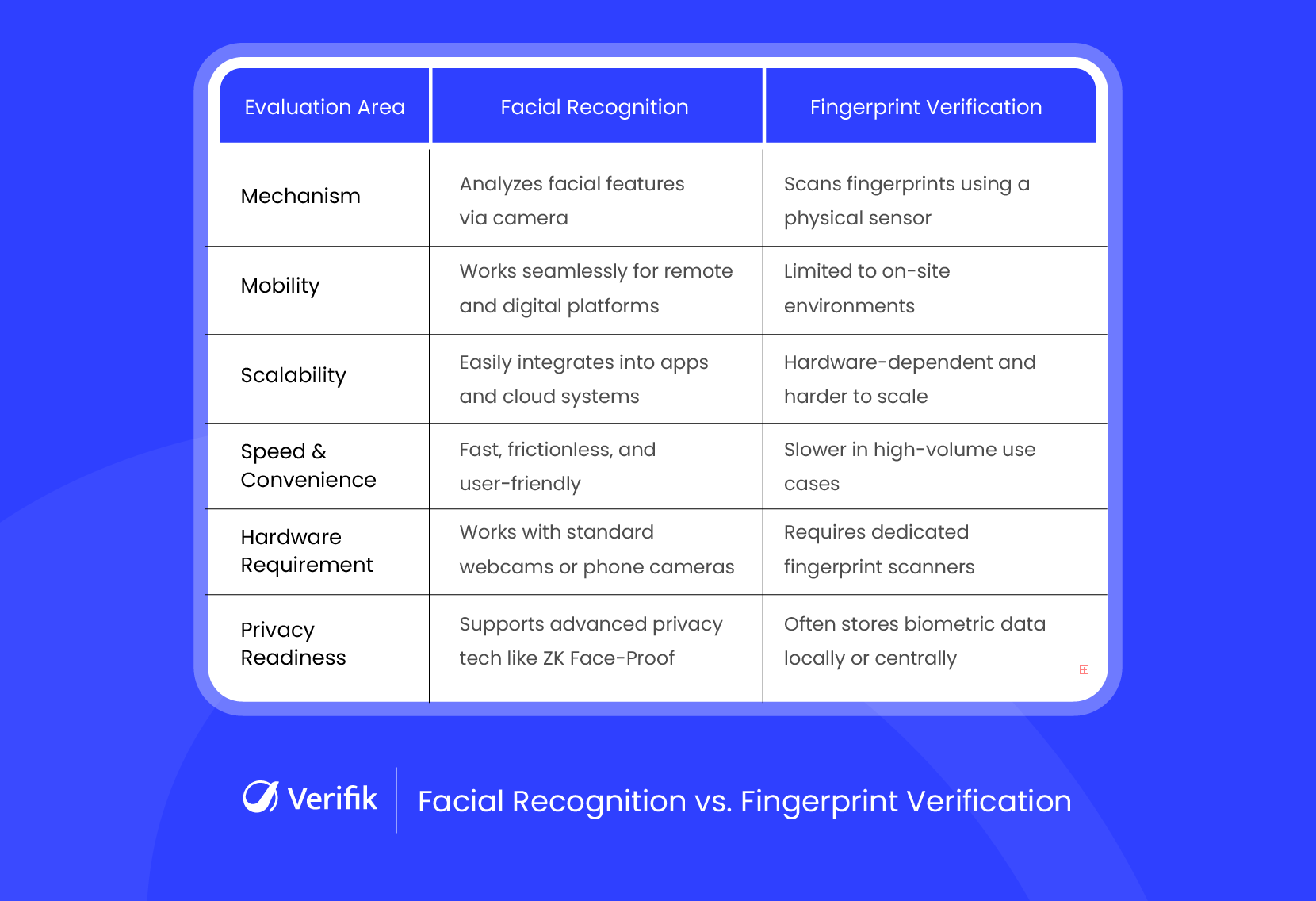
Facial Recognition vs. Fingerprint Identification
Both methods are reliable, but their performance depends on context. Here’s how they compare:
-
User Experience
- Facial recognition offers a smooth, touch-free experience where users are verified simply by facing a camera.
- Fingerprint identification requires physical contact, which can slow down the process in busy or high-turnover settings.
-
Speed & Efficiency
- Facial recognition handles identity checks quickly, making it suitable for environments where speed and flow matter.
- Fingerprint systems take longer, especially when managing large groups or during peak access times.
-
Scalability
- Facial recognition systems can be deployed across multiple locations, devices, and digital channels without much friction.
- Fingerprint systems are more suited to fixed physical access points and are less flexible in remote or digital environments.
-
Environmental Sensitivity
- Facial recognition may face challenges in low light or when faces are partially covered.
- Fingerprint accuracy drops if the skin is wet, dirty, or worn; something common in certain work environments.
-
Remote Verification
- Facial recognition supports remote identity verification, making it ideal for digital platforms and global teams.
- Fingerprint verification requires on-site hardware, limiting its usefulness for remote or mobile-first use cases.
Why Facial Recognition Outperforms Fingerprint Identification
For digital businesses, identity is no longer just about access. It’s about building trust, improving speed, and creating an experience users don’t have to think twice about. Facial recognition helps you do exactly that. It verifies users in seconds, directly through a camera, without requiring any special hardware or extra effort.
Whether you’re onboarding customers in a banking app, authorizing transactions in fintech, or securing access to a cloud-based platform, facial recognition simplifies authentication without compromising on security. It removes friction, reduces drop-offs, and delivers a user experience that feels modern and effortless.
Fingerprint identification, on the other hand, feels rooted in a different era. It depends on physical scanners, making it impractical for fully digital or remote environments. Scaling it across apps or platforms is difficult and often expensive.
Facial recognition, by contrast, grows with your platform. It works across devices, supports remote users, and integrates easily into cloud-based workflows. For businesses operating in a fast-moving digital space, it delivers not only stronger security but also a better user journey.
Final Words
When choosing between facial recognition and fingerprint identification, digital businesses need to weigh security, user experience, and scalability. While fingerprint ID has been reliable for years, facial recognition offers a more seamless, contactless, and flexible solution that fits the digital-first nature of modern businesses. By adopting facial recognition, businesses can enhance security without complicating the user journey, making it the smarter choice for the future of digital identity management.
Ready to Upgrade Your Business Security with Facial Recognition?
Facial verification is no longer just about matching faces, it’s about verifying real users securely, instantly, and without friction.
At Verifik, our facial verification suite is purpose-built for modern digital platforms:
- smartENROLL lets users sign up with just a glance. No forms. No documents. Just real-time verification that works.
- smartACCESS adds serious security to your apps, with facial verification backed by liveness detection, so fake faces don’t get in.
- ZK Face Proof is the world’s first to fuse facial verification with zero-knowledge cryptography. That means identity is verified without storing or revealing any biometric data with just a quick facial scan.
All of these solutions are easy to integrate into your digital platform and are designed to scale with your business.
Want to see how they work? Book a free demo with our team today!