As businesses face rising cyber threats, the choice of authentication methods has become a mission-critical decision. Weak passwords remain a leading cause of data breaches, while biometric authentication is gaining momentum as a more secure, user-friendly alternative. But is it truly safer, or just a trend?
This blog dives deep into the debate of Biometrics vs. Passwords to help you understand which option best secures your enterprise in 2025. Let’s get started!
What are Passwords?
A password is a secret combination of characters (letters, numbers, symbols) created by a user to gain access to digital systems or services. It acts as a single-factor authentication method, relying on what the user knows.
Passwords have been the cornerstone of digital authentication since the inception of computing. They’re designed to act as a digital key and unlock access to a system only if the correct string is presented. However, their effectiveness heavily relies on the user’s habits and the strength of the password itself.
In fact, 81% of data breaches are linked to weak or stolen passwords, making them one of the most common entry points for cyberattacks in digital businesses.

How Passwords Work
- The user sets a password during account registration.
- The password is encrypted (typically hashed) and stored in a server.
- During login, the entered password is hashed and compared to the stored value.
- If it matches, access is granted. Otherwise, it’s denied.
This mechanism is simple, but simplicity is also its weakness when not properly enforced or monitored.
Common Weaknesses of Passwords
- Human Error: Users often pick weak or reused passwords.
- Phishing: Easily stolen through deceptive emails or fake login screens.
- Brute-force Attacks: Automated systems can guess simple passwords.
- Data Breaches: If the hashed password database is stolen, weak hashes can be cracked offline.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a method of verifying identity by analyzing unique biological characteristics of individuals, such as facial features, fingerprints, voice, retina, or even typing patterns. It is a form of inherent factor authentication, relying on who the user is.
Biometrics offer a stronger and more personal layer of security compared to passwords, because they cannot be shared, forgotten, or easily replicated.
How Biometric Authentication Works
- The system initially captures a biometric trait (e.g., face scan, fingerprint).
- This input is converted into a biometric template using mathematical algorithms.
- The encrypted template is stored securely, either locally or in a cloud vault.
- Upon login, the user presents the same biometric trait again.
- The new input is matched against the stored template to grant or deny access based on similarity.
Modern systems integrate liveness detection to ensure the presented biometric data is from a live person and not a spoof (photo, mask, or video).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Passwords
Pros of Passwords
- Universal Compatibility: Works across all platforms and devices.
- Low Initial Investment: Cheap to implement for startups and small apps.
- User Familiarity: No need to educate users as passwords are well-known.
- Easy to Reset: Users can change passwords at will without biometric hardware.
Cons of Passwords
- High Vulnerability: Common target of cyberattacks (phishing, brute-force, credential stuffing).
- User Fatigue: Remembering different passwords for various accounts is burdensome.
- Expensive Maintenance: Constant password resets, support tickets, and policy enforcement drain IT resources.
- Scalability Issues: As user base grows, so do the risks and management headaches.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biometrics
Pros of Biometrics
- Inherently Secure: Unique to each individual, hence reduce the risk of identity theft.
- Improved UX: Users love quick and hassle-free authentication.
- Spoof Prevention: Liveness detection thwarts fraudsters and synthetic identities.
- Reduced Helpdesk Load: Eliminates forgotten password issues.
- Better Engagement: Easier access encourages frequent logins and platform stickiness.
Cons of Biometrics
- Hardware Dependency: Requires devices with cameras, scanners, or microphones.
- Privacy Concerns: Users may hesitate to share sensitive biometric data.
- Regulatory Complexity: GDPR, BIPA, and CCPA impose strict rules around biometric data usage and storage.
- Irrevocability: Unlike passwords, you can’t reset a fingerprint or retina.
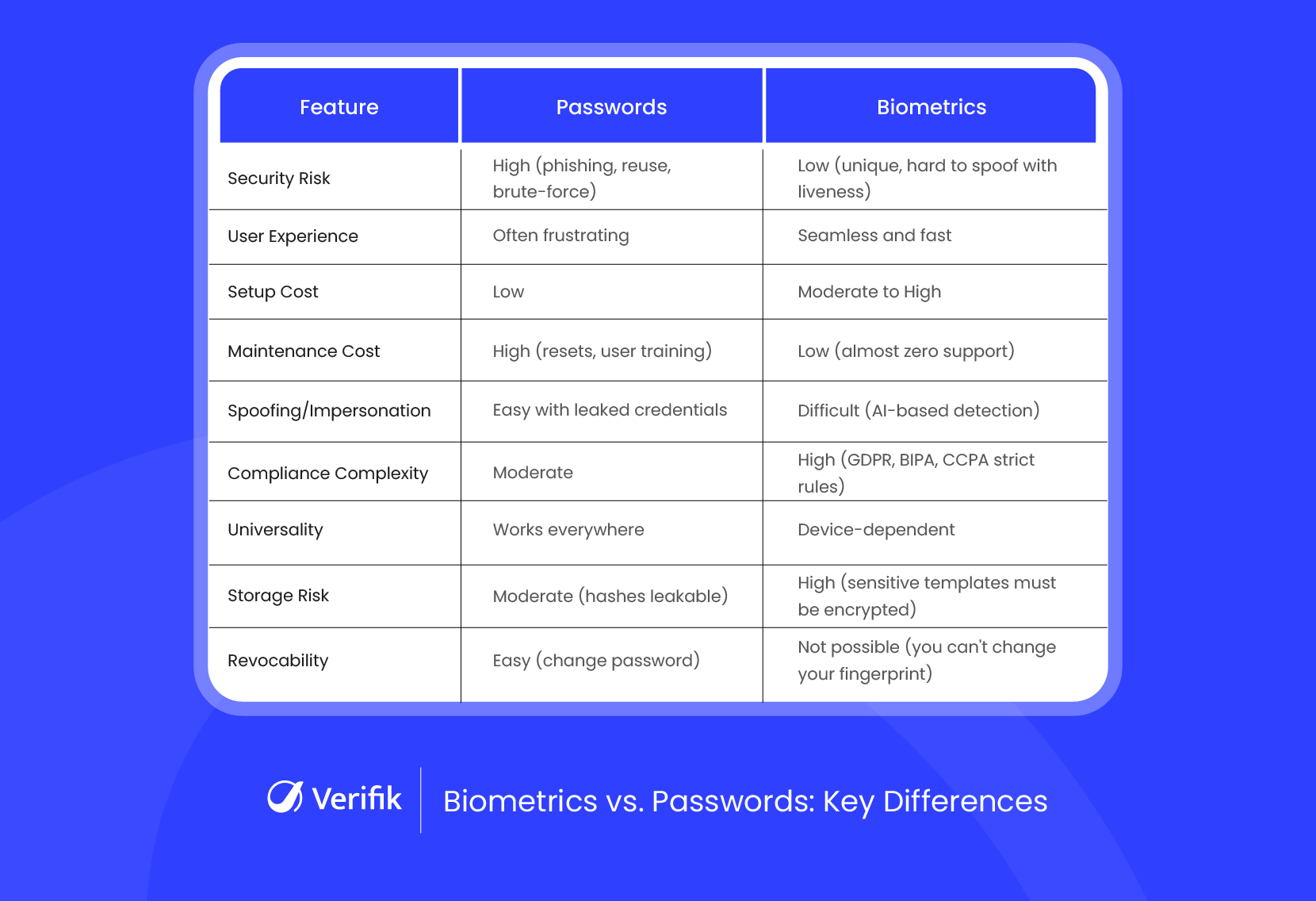
Biometrics vs. Passwords: A Feature-by-Feature Comparison
Let’s break down how passwords and biometrics perform across the key features that matter most for digital platforms.
1. Security Risk
Passwords:
Passwords are easy targets for attackers. Many users create weak passwords or reuse the same one across different websites. If one account gets hacked, others become vulnerable too. Phishing emails can trick users into giving them away, and brute-force attacks can guess them in seconds.
Biometrics:
Biometric data is much harder to steal or guess. It’s based on your physical traits, like your face or fingerprint, which are unique to you. Even if someone tries to trick the system with a photo or recording, most biometric systems now include liveness detection to make sure the person is real and present.
2. User Experience
Passwords:
Many users struggle to remember complex passwords. They often need to reset them, especially if they don’t log in often. This creates friction during signup or login and can even lead to users abandoning your platform.
Biometrics:
Biometric login is quick and easy. The user just looks at their screen or places a finger. No need to remember anything or go through extra steps. This smooth experience makes it more likely that users will come back and trust your platform.
3. Setup Cost
Passwords:
Passwords are easy to set up and require minimal investment. But this “low-cost” solution often becomes expensive in the long run due to security issues and user support.
Biometrics:
Biometric systems require a bit more planning and integration. You’ll need the right APIs or SDKs, and devices must support biometric input. But the benefits in security, speed, and user satisfaction justify the upfront investment, especially as modern devices come equipped and ready.
4. Maintenance Cost
Passwords:
Ongoing support for passwords can drain your resources. Think of the time and money spent on password resets, user complaints, and internal IT escalations.
Biometrics:
Biometrics need almost no maintenance after the initial setup. Users don’t forget them, and the support team doesn’t have to handle constant login issues. This saves your platform time and money over the long term.
5. Spoofing and Impersonation
Passwords:
If someone knows your password, or can guess it, they can log in as you. There’s no way for the system to know it’s not the real user. This makes impersonation very easy.
Biometrics:
Impersonating a biometric trait is far more challenging. With intelligent anti-spoofing techniques now embedded in many solutions, even attempts using photos, videos, or deepfakes are detected and blocked.
6. Compliance Complexity
Passwords:
Password systems need basic protection under general data privacy laws. They’re easier to manage from a compliance point of view, especially for small companies.
Biometrics:
Biometric data is personal and sensitive. This means you must follow stricter rules under laws like GDPR or CCPA. But many modern biometric providers now offer built-in tools that help you manage user consent, store data securely, and stay compliant.
7. Universality
Passwords:
Every platform and device can use passwords. You don’t need any special hardware, which makes them accessible to everyone, everywhere.
Biometrics:
Biometric systems need devices with the right hardware, like a front camera or fingerprint scanner. The good news is that most modern smartphones, laptops, and tablets already come with these built-in, so for digital-first users, it’s rarely a problem.
8. Storage Risk
Passwords:
Passwords are stored as hashes in databases. If hackers steal these hashes, they can try to crack them or use them in attacks on other websites. This puts both users and platforms at risk.
Biometrics:
Biometric data is stored as encrypted templates in modern privacy-first verification solutions. These cannot be easily reversed or used to access other accounts. Even if someone manages to steal a template, it’s almost impossible to use it for impersonation without a full system breach.
9. Revocability
Passwords:
If a password is leaked, you can change it instantly. This makes it easier to fix a security problem.
Biometrics:
You can’t change your face or fingerprint. But because they’re so hard to fake in the first place, they’re less likely to be compromised. When built with fallback options (like PINs or OTPs), biometric systems remain safe and reliable.
What This Means for Digital Platforms
Digital platforms today are expected to offer both strong security and a smooth user experience. Biometrics meet that expectation by reducing fraud and making access faster and more intuitive for users.
Passwords, though familiar, have become fragile in the face of growing cyber threats. Asking users to remember something, type it out, and reset it when forgotten is no longer a secure or user-friendly solution.
Biometric authentication, especially when combined with liveness detection, offers a more secure and user-friendly alternative. It ensures that the person logging in is not only the right user but also physically present at the time of login.
More importantly, platforms that adopt privacy-first solutions, such as zero-knowledge verification methods that don’t store raw facial data, show a clear commitment to protecting user identity without compromising convenience.
Choosing the right login method shows users how seriously you take their safety. And that trust makes all the difference.
Final Thoughts
Passwords are easy to forget, easy to steal, and hard to secure. Most breaches today trace back to poor password hygiene. Biometrics change that by tying access to something users are; not something they remember. With liveness detection and strong data protection, biometrics offer a much stronger defense.
If security matters to your platform, it’s time to move beyond passwords.
How Verifik Can Help
As fraud gets smarter and users expect instant access, passwords are showing their limits. Verifik gives digital businesses a better way forward with our modern and secure biometric solutions.
Our most loved solutions by digital-first companies include:
- ZK Face Proof – Verify users with facial biometrics, without storing any sensitive data.
- smartACCESS – Secure access control that blocks fraud and ensures only verified users get through.
- smartENROLL – Onboarding made seamless, secure, and real-time, with full KYC compatibility.
Whether you’re building a platform in fintech, healthcare, e-commerce, or any other digital space, our solutions are flexible, compliant, and built for scale.
Let us show you what secure, user-first verification can really look like. Schedule a free consultation with our experts today to explore your options!