In a world where digital identity fraud is growing exponentially, businesses are under immense pressure to verify users with speed, accuracy, and compliance. Traditional identity verification methods, like passwords, ID documents, or security questions, are no longer sufficient to protect against sophisticated fraud.
Biometric verification is emerging as the gold standard. From securing fintech apps to enabling frictionless onboarding for e-commerce platforms, it’s transforming how businesses authenticate users.
This blog explores how businesses can successfully implement biometric verification, with guidance on choosing the right tools and handling common challenges.
What is Biometric Verification?
Biometric verification is a process that identifies individuals based on their unique biological traits, like fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voice. Because these characteristics are uniquely inherent by each person, they are highly secure and nearly impossible to replicate.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on passwords, PINs, or physical ID cards, biometric verification ties access directly to who a person is, not what they know or have. This makes it a powerful tool for businesses looking to strengthen security, reduce fraud, and simplify user access across physical and digital environments.
Types of Biometric Verification
Different biometric technologies serve different purposes. The most common biometric verification methods include:
- Facial recognition – Quick and easy to use on any device with a camera
- Fingerprint scans – Used more often in hardware (phones, kiosks)
- Voice recognition – Useful in phone-based interactions
- Iris scanning – Highly accurate, but usually reserved for high-security environments
Of all the biometric methods, facial recognition has become the most common, and for good reason. It’s fast, easy to use, and works on devices people already have, like phones and laptops. Unlike fingerprints or iris scans that need special hardware, facial recognition just needs a camera, which makes it far more accessible for everyday use.
For businesses, adopting biometric verification isn’t just about better security, it also improves how users experience your services. Less friction, fewer forgotten passwords, and more confidence all around.
Why Businesses Are Adopting Biometric Verification
The global biometric system market is expected to reach $84.5 billion by 2029. Businesses of all sizes are turning to biometric verification to solve key challenges like fraud, slow customer onboarding, and poor user experience. Below are the main reasons why this technology is gaining rapid traction.

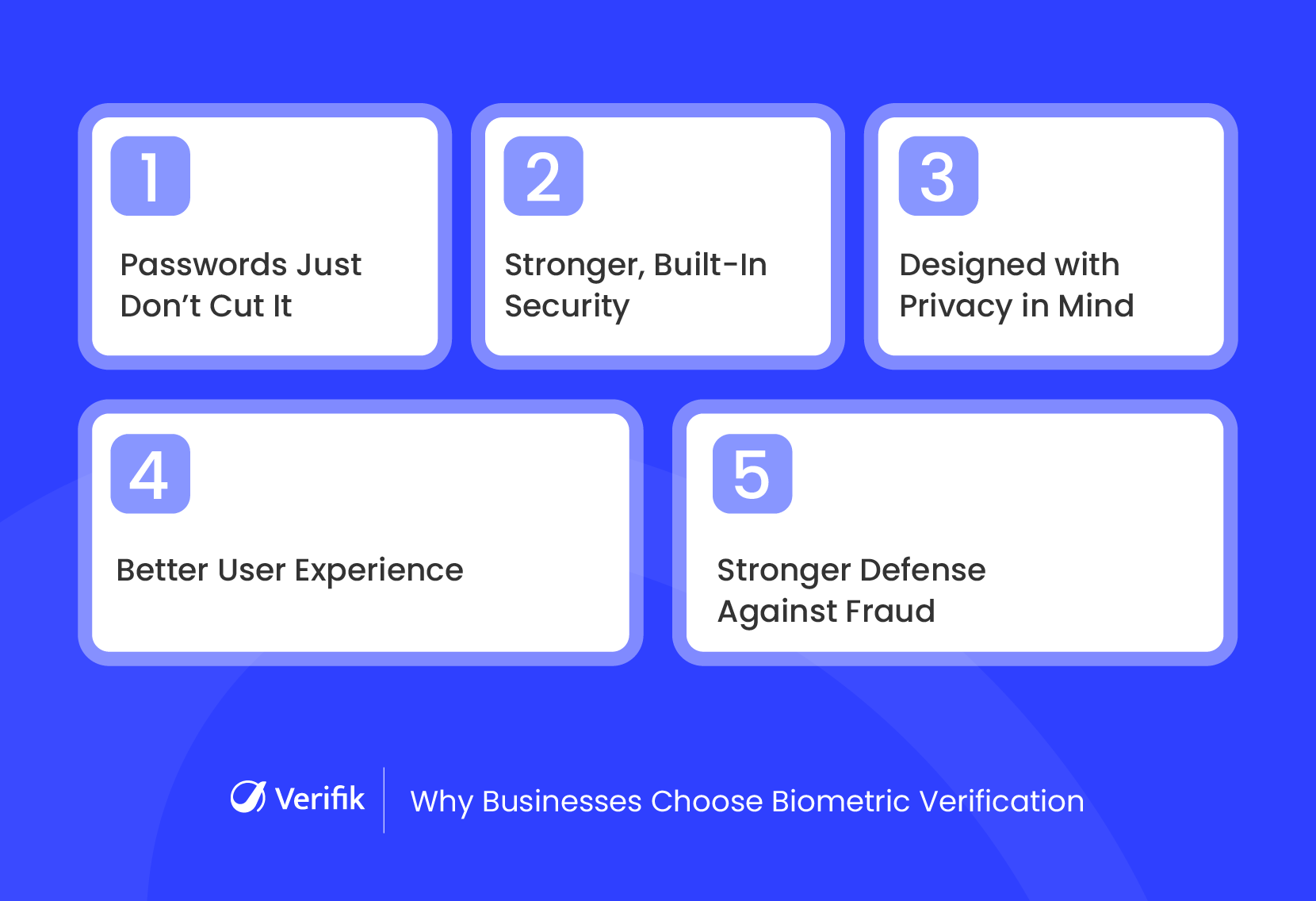
1. Passwords Are No Longer Enough
Passwords have always been the weak link. They’re either too simple and easy to crack, or so complex that people forget them. For businesses, this creates ongoing headaches: higher support costs, lost conversions, and increased vulnerability to data breaches. Password resets alone drain both time and resources. Biometric verification removes this dependency entirely by relying on something people always have; themselves.
2. Built-In Stronger Security
Biometrics like facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice recognition add a layer of protection that’s incredibly difficult to replicate or bypass. Unlike PINs or ID cards, biometric traits can’t be shared, stolen, or guessed. This makes them ideal for industries where security and identity accuracy are non-negotiable, from finance to healthcare and even employee access control.
3. Privacy-Focused Verification
Protecting user privacy is a top concern for businesses adopting biometric verification. One of the most innovative solutions addressing this is ZK Face Proof, which combines facial recognition with zero-knowledge cryptography in a unique way. With ZK Face Proof, businesses can verify users quickly through a simple facial scan without any need to store their raw or sensitive facial data. By keeping personal information secure, this privacy-first verification technology not only helps businesses meet strict regulations like GDPR but also builds stronger trust with customers.
4. Better Experience for End Users
Biometric verification isn’t just about security, it’s also about convenience. Logging in with a face scan or fingerprint is faster, smoother, and far more intuitive than typing a password or waiting for an OTP. This frictionless experience boosts user satisfaction, shortens onboarding time, and increases engagement. And when your customers or employees find it easier to interact with your systems, it reflects positively on your brand.
5. Cutting Down Fraud and Errors
In sectors like banking, crypto, and e-commerce, fraud is a constant concern. In 2024, online payment fraud caused over $44.3 billion in losses globally for e-commerce alone. Biometric verification helps reduce these risks by making it much harder for imposters to access accounts or for users to make identity errors. This not only protects your business but also builds stronger trust with customers. Plus, it supports stronger KYC and AML compliance. It’s also an effective way to strengthen your KYC and AML processes.
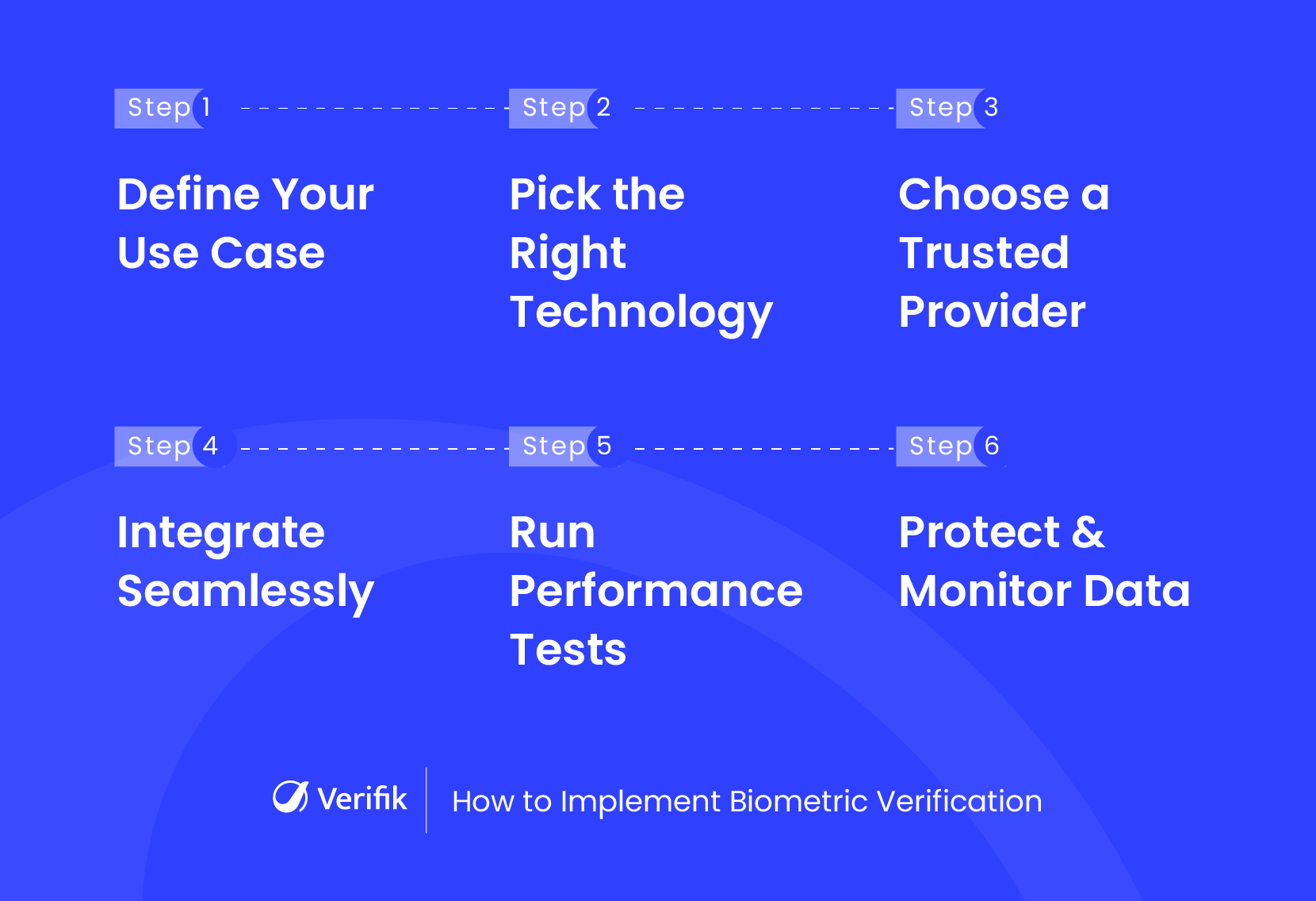
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Biometric Verification
Implementing biometric verification in your business may sound complex, but breaking it down into clear steps can make the process smooth and effective. Here’s a practical guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Identify Your Use Case
Start by understanding where biometric verification can bring the most value. Are you trying to speed up user onboarding? Improve the security of high-value transactions? Or verify employee attendance at physical locations? Clear use cases could include secure system access for internal users or automated age verification for consumer platforms. Knowing your goal will help you design the user journey and set the right expectations.
Step 2: Choose the Right Biometric Technology
Once your use case is clear, select the biometric method that best suits your audience and platform. Facial recognition is popular for mobile and web apps due to ease of use and camera accessibility. Fingerprints may be more practical in physical settings like office entrances or factory floors. Voice recognition works well in call-based environments. Choosing the right method impacts user adoption and technical integration.
Step 3: Select a Reliable Biometric Solution Provider
Evaluate potential vendors based on more than just cost. Look at their track record for:
- Accuracy and false match rate: High-accuracy systems reduce friction and prevent fraud.
- Speed and scalability: Fast verification is critical for a seamless user experience, especially at scale.
- Compliance certifications: Ensure providers are compliant with standards like ISO, GDPR, or SOC 2.
- Liveness detection: Real-time detection of spoofing attempts is non-negotiable.
- Integration support: APIs and SDKs should be well-documented and easy to implement.
At Verifik, we check all those boxes. Our privacy-first technologies, like Zero Knowledge Proof and the world’s most advanced and exclusive ZK Face Proof, deliver quick, secure, and accurate identity verification in just seconds using a simple facial scan, all without storing any sensitive user data. Plus, our team is here to support you through every step of implementation and beyond.
Step 4: Integrate with Your System
Choose whether your deployment will be cloud-based or on-premise, depending on data residency and security needs. Use the provider’s API or SDK to embed the biometric verification flow into your web app, mobile platform, or backend service. Ensure the process fits naturally into the user journey, for instance, by integrating face verification right after sign-up or before confirming a payment.
Step 5: Test for Performance
Before going live, run a pilot with real users. Test for matching accuracy, especially across different device types, lighting conditions, and demographic groups. Track any false positives or negatives. Also pay close attention to user experience, like how intuitive the flow is, how long it takes, and where drop-offs occur. A well-run pilot gives you insights to fine-tune the implementation.
Step 6: Secure Biometric Data and Monitor Usage
Treat biometric data like gold. Use strong encryption both in transit and at rest. Store templates in tamper-proof databases and maintain logs of every access attempt. Set up anomaly detection systems to alert you of unusual patterns, such as repeated failures from the same IP or sudden location shifts. Monitoring helps you stay proactive against emerging threats.
Common Challenges in Biometric Verification and How to Handle Them
Biometric verification adds a powerful layer of security, but it’s not without complications. Whether you’re verifying identities for secure logins or onboarding users remotely, certain challenges tend to surface. Addressing these early can save time, reduce friction, and build greater user trust.
-
Spoofing and Deepfakes
Spoofing attacks have become more advanced with the rise of AI-generated content. Fraudsters now use realistic images, videos, or even deepfake technology to impersonate real users and bypass biometric systems that rely only on surface-level image matching. If a system lacks proper safeguards, like verifying if a face is live and present in real time, it becomes vulnerable to these deceptive tactics.
To counter this, strong liveness detection should be part of your biometric stack. Instead of just recognizing faces, these systems assess subtle movements like blinking, head tilts, or changes in lighting on the skin; clues that reveal whether the input is coming from a real, live person. This extra layer doesn’t add friction to the user experience but drastically reduces the chance of impersonation going undetected.
-
Bias in the System
Bias in biometric systems isn’t always obvious, but it can have serious consequences. Many algorithms perform poorly for users with darker skin tones, older age groups, or those with facial features that aren’t well represented in the data used to train the model. These disparities can lead to higher error rates and exclusion for specific populations, damaging both trust and accessibility.
Addressing this starts with choosing solutions that have been tested across diverse demographics. Inclusive datasets, regular performance audits, and published accuracy metrics all help ensure a more equitable experience. When everyone can verify their identity with the same level of success, the system becomes more trustworthy and truly scalable.
-
User Concerns About their Data
Even with a secure and accurate biometric system, user concerns about surveillance and data misuse can be a major barrier. The fear of losing control over biometric data, like a face or fingerprint, is real for some users, especially if the system stores it indefinitely or doesn’t explain how it’s used. These doubts can reduce adoption, no matter how secure the technology is.
The solution lies in transparency and control. Users should be clearly informed about what data is collected, how it’s stored, and whether it can be deleted. Offering privacy-focused alternatives, like verification methods that don’t store raw biometric data, can make a real difference. When people feel their data is handled responsibly, they’re far more likely to trust and use the system.
Final Thoughts
Biometric verification is a smart way to protect your business while improving the customer experience. It’s not without challenges, but with careful planning and the right partner, it can add lasting value.
Verifik makes this transition easier by offering secure, privacy-focused, and easy-to-integrate biometric solutions. Whether you’re a startup or scaling enterprise, implementing biometrics the right way can help you build trust, reduce fraud, and stay ahead of regulation.
Get in touch with us today or schedule a free consultation to see how we can support your goals!